Early diagnosis and treatment is
the best prevention for thyroid cancer!
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland located in the middle of the neck,
wrapped around the windpipe underneath the forward-protruding
collar bone (thyroid cartilage), which produces thyroid hormones.
Thyroid hormones regulate your body's metabolism and play
an important role in the autonomic nervous system.
Diseases of the Thyroid Gland
-
01
Abnormalities in thyroid function
Hyperthyroidism
The thyroid gland becomes enlarged and produces and secretes too many hormones, causing the body to produce and use more energy than it needs. The body becomes hot, sweats profusely, loses weight, and the autonomic nervous system becomes excited, causing the heart to pump more and the pulse to beat faster.
Hypothyroidism
A condition in which the production and secretion of thyroid hormones is reduced, resulting in sluggishness, cold sensitivity, weight gain, and a slow heart rate.
-
02
Benign thyroid lumps (thyroid nodules)
Thyroid nodules are categorized as benign or malignant and are palpable only when they grow to a certain size. It is a very common condition, especially in women, and can occur at any age, but is more common in older people. An ultrasound of the thyroid gland can detect even small nodules.
-
03
Types and frequency of thyroid cancer
-
Papillary cancer
The most common cancer,
about 90% of the time,
with the best prognosis -
Follicular cancer
About 10% of the time,
it is often found in advanced cancer
and metastasis is a concern. -
Medullary cancer
Rare in the East, occurring in 1-2% of cases, often slow-growing,
with a good prognosis if it does not metastasize. -
Anaplastic cancer
Very rare, the tumor grows very rapidly
and causes difficult symptoms
such as shortness of breath,
and has the worst prognosis.
-
Diagnostic procedures for the thyroid
-
Thyroid hormone test
It tests the thyroid regulatory function of the pituitary gland and is the first to reflect changes in thyroid function, so measurement of blood TSH is useful for early detection of hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, and is used for differential diagnosis in rare cases of thyroid diseases caused by the pituitary gland.
-
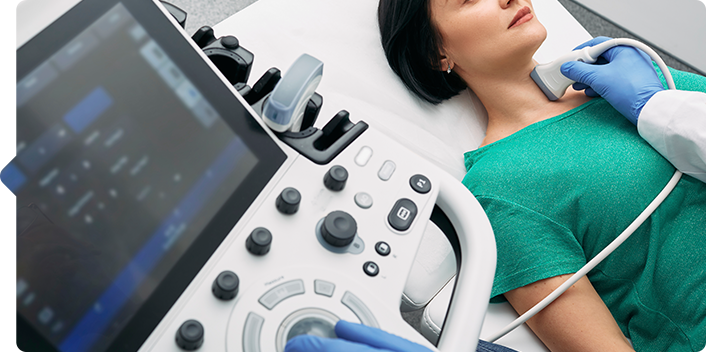
Thyroid ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound can show the size, shape, location, and number of nodules, as well as cystic changes in the nodule (blood or water collecting in the nodule) or cysts (watery nodules).
-

Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
This is a test in which cells are aspirated (pulled out) from the thyroid nodule with a syringe, stained, and viewed under a microscope. It is usually done with a syringe under simple skin anesthesia. It's a simple test that takes less than a minute or two to perform, making it an essential test to determine if a thyroid nodule is cancerous.
-
Thyroid scan
This is a basic test to determine the shape of the thyroid gland and involves the administration of a radioactive isotope called radioactive iodine or technetium and imaging of the thyroid gland. With radioactive iodine, you usually take the radioactive iodine by mouth and the scan is usually done a few hours to a day after you eat. With technetium, the isotope is injected intravenously and the scan is taken 20 to 30 minutes later.
Thyroid Treatment Methods
-
01
Thyroid Hormone Therapy
Thyroid hormone is sometimes taken to reduce or eliminate the size of thyroid nodules, but the duration is too long (6 months to a year or more), the effectiveness is not certain, and the nodules may return when the treatment is stopped.
-
02
Surgery
Surgery requires general anesthesia, a long hospital stay, and most importantly, a scar on the front of the neck. However, if the thyroid nodule is suspected of being cancerous, surgery should be performed.
-
03
Radiofrequency ablation (radiofrequency thermotherapy)
Radiofrequency ablation is a method that is widely used in the world to identify the location of the nodule in the thyroid gland by ultrasound examination, and then insert the radiofrequency ablation needle into the nodule and apply high frequency to generate friction heat, which causes the tumor to be necrotic. It has been used for the treatment of benign and malignant tumors in various parts of the human body, and recently it has been clinically proven and used for the removal of thyroid nodules.
Advantages of radiofrequency heat treatment
- A.
It can be completely removed without leaving a scar on the neck.
- B.
No hospitalization or general anesthesia is required.
- C.
You can return home after a short rest (2-3 hours) and resume your daily activities immediately.
- D.
Almost no side effects.
Disadvantages of radiofrequency heat therapy
- A.
The nodules do not disappear immediately because it burns them away.
The volume of the nodule is reduced by 50% one month after the treatment, and after one year, it is reduced to 20% and no longer grows. - B.
Approximately 1-5% of patients may recur, but if they do, they can be treated by repeating radiofrequency thermal therapy.
- A.















