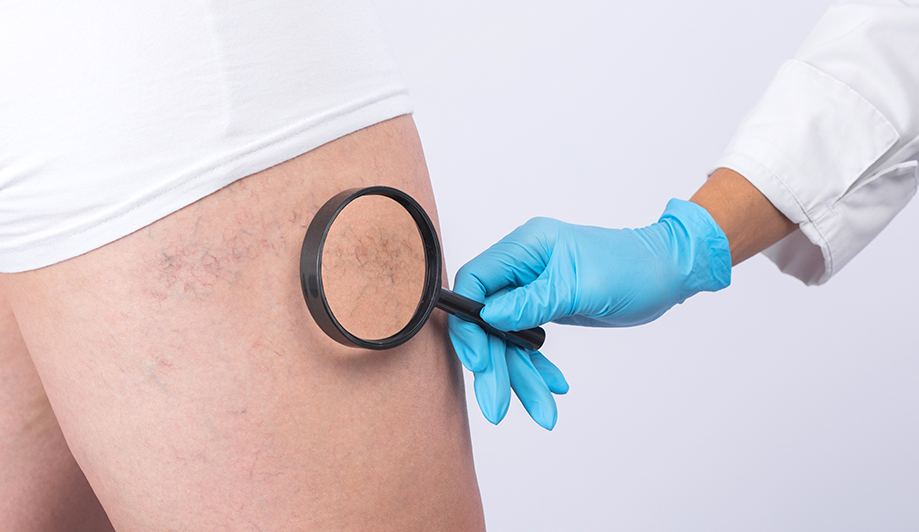
Varicose veins are damaged and refluxing veins in the lower extremities.
Often described as having "tendons" sticking out of your legs, varicose veins are damaged and refluxing veins in the lower extremities due to factors such as prolonged standing.
This causes the veins in the legs to bulge in a tortuous, snake-like or pod-like shape, causing pain, tingling, swelling, and cramping in the lower extremities. There are six clinical stages of varicose veins, ranging from telangiectasias, which look like thin spiderwebs, to active skin ulcers, which are characterized by skin damage and bleeding in the ankle area.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
People often come to us because they notice that the veins in their legs are bulging in a squiggly, snake-like or beaded shape, or that they feel self-conscious when wearing short pants or skirts due to the presence of capillaries, dark stains, or bruising.
-
 Fatigue and pain in the legs, especially in the afternoon, which is worse than in the morning, and the symptoms are relieved when the legs are elevated or resting.
Fatigue and pain in the legs, especially in the afternoon, which is worse than in the morning, and the symptoms are relieved when the legs are elevated or resting.
-
 The bulging blood vessels in your legs may feel tender, pulling, tickling, or burning.
The bulging blood vessels in your legs may feel tender, pulling, tickling, or burning.
-
 You wake up with cramps in your calves while you sleep.
You wake up with cramps in your calves while you sleep.
-
 In the afternoon, your feet and ankles may swell or become tender around the ankles. At first, the swelling is only in the afternoon, but gradually the swelling increases in time and severity.
In the afternoon, your feet and ankles may swell or become tender around the ankles. At first, the swelling is only in the afternoon, but gradually the swelling increases in time and severity.
-
 If left untreated, the ankle to inner calf area may become darkly colored and dermatitis may develop that does not heal well.
If left untreated, the ankle to inner calf area may become darkly colored and dermatitis may develop that does not heal well.
In addition to the discoloration and dermatitis, the legs also become easily wounded, and once wounded, they do not heal well.
In severe cases, skin ulcers, skin necrosis, and even spontaneous blood vessel bursting and bleeding occur on the legs.
Causes of Varicose Veins
-

Family history
People with a family history of varicose veins have a higher incidence.
-

Trauma, deep vein thrombosis
Trauma and thrombosis can cause many varicose veins in the lower extremities.
-

Age
The elasticity of blood vessels decreases with age and increases with degeneration of the calf muscles.
-

Food
Consuming foods high in fat or cholesterol can obstruct the flow of arteries or veins.
-

Pregnancy
Hormonal changes also occur, and in addition, the enlarged uterus compresses the veins, causing poor venous circulation, which may lead to varicose veins.
-

Posture
Lack of exercise, such as prolonged standing without movement and prolonged sedentary behavior, can slow blood circulation and lead to varicose veins.
-

Smoking
Smoking can increase blood pressure, which can lead to the development of varicose veins.
-

Exercise
Increased abdominal pressure, such as excessive abdominal exercises, can lead to varicose veins.
-

Gender
Women may be more likely to develop varicose veins than men due to female hormones, etc.
-

Others
Treatment of Varicose Veins
-
01
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatments include wearing medical compression stockings and taking flavonoid-based medications such as diosmin.
Both of these methods help improve circulation in the veins of the legs, which can relieve many of the symptoms of varicose veins. -
02
Angiosclerotherapy
Angiosclerotherapy is a treatment in which sclerosing ageat is injected intravenously with a syringe.
It is applied to thin varicose veins such as spider veins and reticular veins that are difficult to treat with surgery, and is still widely used as an adjunctive therapy to other treatments. Some skin discoloration may occur after the injection, but this usually fades gradually after three to six months. -
03
Ambulatory phlebectomy
A small 2-3 mm incision is made in the skin and a curved needle-like instrument called a hook is used to pull the vein out and remove it, leaving only very small scars after the procedure. Ambulatory phlebectomy is often used in conjunction with high-level ligation and stripping, laser therapy, and radiofrequency ablation, which are discussed below.
-
04
High-level ligation and stripping
This method involves cutting off the vein causing the varicose veins at the origin and then peeling them off. It is the most radical method of treating varicose veins, but it has the disadvantages of leaving more scarring than the minimally invasive procedures below, high postoperative pain, and the risk of nerve damage during the removal of the veins.
-
05
Endovenous laser
Endovenous laser treatment is a surgical procedure in which a thin laser conduit is inserted into the varicose vein and irradiated with laser light to generate heat to block the vein, causing the varicose vein to gradually degenerate and disappear.
It is now the standard of treatment for varicose veins, with less post-operative pain and virtually no scarring compared to high-level ligation and stripping. -
06
Clarivane
This treatment uses a sclerosant that does not cause physical or thermal damage, resulting in a quick recovery period and little pain and scarring.
It is currently a widely practiced treatment in the United States and European countries. -
07
Benacil
Unlike endovenous laser treatment or radiofrequency ablation, which apply heat to the blood vessels to close them, Benacil is a treatment that uses a medical-grade bioadhesive called cyanoacrylate, which is injected into the varicose veins to close them. Unlike endovenous laser therapy or radiofrequency ablation, which apply heat to the blood vessels, the use of a bioadhesive eliminates pain, bruising and the need to wear medical compression stockings after the procedure, making it an emerging treatment option.
-
08
Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is a surgical procedure in which a radiofrequency tube is inserted into a varicose vein and radiofrequency waves are generated to close the vessel. The surgical method and difficulty are very similar to endovascular laser treatment, but unlike endovascular laser treatment, it is an advanced treatment that reduces the risk of burns and postoperative pain by limiting the heat generation within the body's tissues to within 120 degrees centigrade with a temperature sensor at the end of the radiofrequency tube. However, the cost of the disposable radiofrequency tube is somewhat higher than endovascular laser therapy.
*Side effects such as pain and bleeding may occur in rare cases depending on the patient's condition.















