Currently, Korea is experiencing a
steady increase in breast cancer cases.
However, to date, there is no definitive cause of breast cancer.
Unfortunately, there is no definitive cause of breast cancer that
we can say "breast cancer is caused by this, so don't do this".
Causes of increased breast cancer risk
-
 Having a mother or sister with breast cancer.
Having a mother or sister with breast cancer.
-
 Early menarche and late menopause, which means that female hormones affect the body for a longer period of time.
Early menarche and late menopause, which means that female hormones affect the body for a longer period of time.
-
 Westernized lifestyle, such as singleness, later marriage, increased age of first birth, and fewer children.
Not breastfeeding.
Westernized lifestyle, such as singleness, later marriage, increased age of first birth, and fewer children.
Not breastfeeding.
-
 Obesity due to westernized dietary habits, which causes female hormones to become unbalanced.
Obesity due to westernized dietary habits, which causes female hormones to become unbalanced.
-
 Obesity due to westernized dietary habits, which causes female hormones to become unbalanced.
Obesity due to westernized dietary habits, which causes female hormones to become unbalanced.
-
 Obesity or excessive consumption of alcohol and animal fats.
Obesity or excessive consumption of alcohol and animal fats.
-
 Taking oral contraceptives.
Taking oral contraceptives.
-
 Long-term postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy.
Long-term postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy.
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
Many women experience breast pain before their period, so it's often unclear what level of pain is pathological.
In fact, 90% of breast pain is mild and temporary, and the symptoms usually go away on their own after a doctor confirms that the breast pain is not caused by breast cancer. Only in the remaining 10% of patients does the pain persist for more than a week or interfere with their lives, and only then is it a candidate for medication through a breast clinic.
-
Cyclical pain
Usually worst before menstruation, decreases once menstruation starts, and on average, both sides hurt about 5 days a month, although it's not uncommon for only one side to hurt. It's hard to pinpoint where the pain is, but it's usually centered around the nipple, with a lot of pain on the outside and top. "Heavy, aching, tingling, stabbing. It jolts when something touches it. It's uncomfortable..." and in severe cases, the pain can radiate into the armpit and up the arm.
-
Non-cyclical pain
Irregular pain that occurs outside of the menstrual cycle and is rarer than cyclic pain, mostly unexplained, more common after the age of 40, and can occur after menopause. The area of pain can be pointed out relatively clearly, usually only in one breast, and the pain is described as "sharp, like a knife stabbing...", etc. ..." and the pain is often constant. If you experience this non-cyclical pain and feel a palpable lump in your breast, you should see a breast specialist to differentiate it from breast cancer.
How breast cancer is diagnosed
However, a mammogram is performed at the same time as a breast exam because reports suggest that 7 to 10 percent of women with early-stage breast cancer have breast pain at the same time.
-

Self-Examination
Breast cancer is one of the rare diseases that you can identify abnormalities by palpating yourself. It is "an important screening method for women if they are unable to get regular checkups."
-

Clinical Examination by a Doctor
While a physical examination alone can't completely differentiate between the presence or absence of a lesion, understanding the hardness and shape of the breast, which varies from person to person, can improve accuracy. However, it's difficult to detect small tumors that even doctors can't feel, which makes imaging even more important.
-

Mammograms
Mammograms are very sensitive in detecting breast cancers that cannot be palpated, making them the primary screening method for breast cancer prevention in asymptomatic women.
-
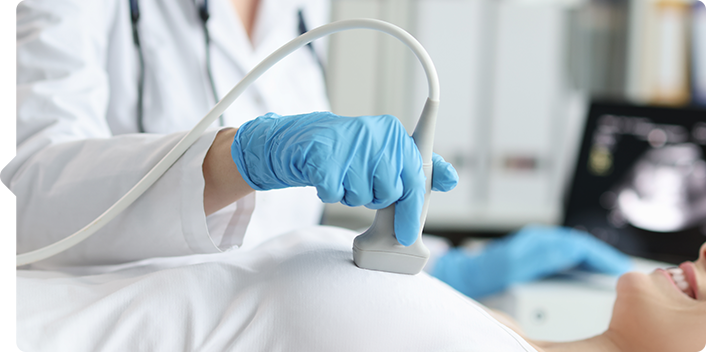
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound is an important test in breast cancer screening. It is used to further investigate lesions found on mammography or palpation, or as an adjunctive test in the case of dense breasts on mammography. If the malignancy of a mass is difficult to distinguish by ultrasound, follow-up mammography or ultrasound is performed to observe changes, and biopsy is required if further malignancy is suspected.
Breast Aspiration Lumpectomy
Advantages of Breast Aspiration Lumpectomy
 No stitches are needed where the needle is inserted, so there is little scarring of the breast.
No stitches are needed where the needle is inserted, so there is little scarring of the breast. It can be an alternative to surgery in benign lumps.
It can be an alternative to surgery in benign lumps. It is performed under local anesthesia, so there is little pain.
It is performed under local anesthesia, so there is little pain.  There is little physical and emotional distress from the surgery.
There is little physical and emotional distress from the surgery. The bump is completely removed in one procedure and the tissue is removed with minimal resection of the surrounding normal tissue.
The bump is completely removed in one procedure and the tissue is removed with minimal resection of the surrounding normal tissue. It is very suitable for those with dense and firm breasts like Korean women.
It is very suitable for those with dense and firm breasts like Korean women. The diagnostic accuracy for cancer is 100%, making it the most reliable test method.
The diagnostic accuracy for cancer is 100%, making it the most reliable test method.















