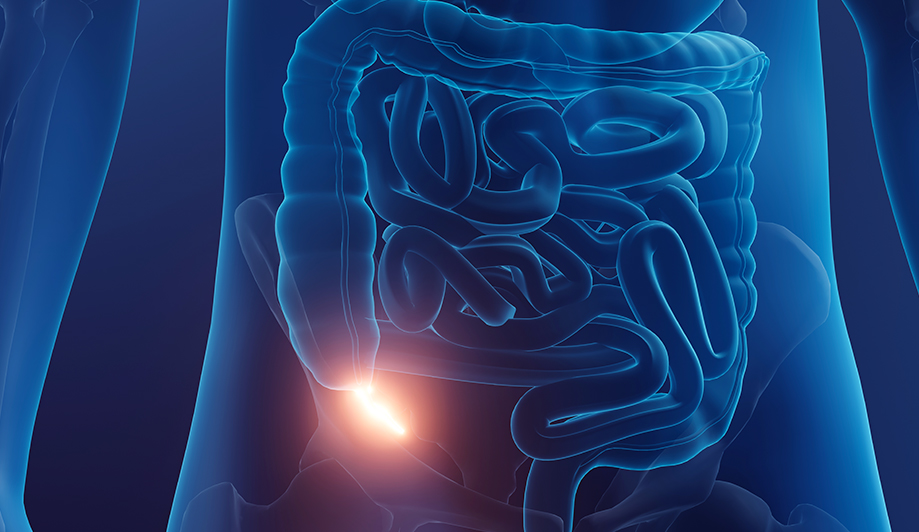
Appendicitis
is the most common cause of
abdominal pain
requiring surgery in clinical practice.
Appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the appendix,
the most common cause of abdominal pain requiring surgery in clinical practice.
It is commonly referred to as appendicitis because
the appendix is attached to the cecum, the first part of the large intestine.
-
01
Symptoms of Acute Appendicitis
Symptoms of acute appendicitis may start with a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium or upper abdomen, followed by nausea, loss of appetite, and indigestion, and then gradually progress to pain in the right lower abdomen as the inflammation progresses.
The pain in your right lower abdomen will be painful to press on, the area will ring when you cough, and you'll feel pain when you walk or run, and most of the time it's not very severe.
Sometimes you may have a low-grade fever, like body aches. -
02
Treatment of Acute Appendicitis
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is the only treatment for both children and adults.
The treatment of acute appendicitis is surgical excision... Due to the varying anatomical location of the appendix, the diagnosis and surgery can be quite straightforward, or it can be challenging even for experienced surgeons.
The timing of surgery depends on the severity of the symptoms, and if the patient is not in critical condition and is not dehydrated, it is recommended to operate immediately. If more than three days pass, the appendix may rupture, causing an abscess around the appendix, or the inflammation may spread into the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis, in which case surgery becomes very complicated.
Complications include perforation, peritonitis, appendix abscess, intra-abdominal abscess, and portosystemic inflammation.















